New World Screwworm

New World screwworm (NWS) infestation occurs when NWS fly larvae (Cochliomyia hominivorax) infest the flesh of living mammals and, less commonly, birds. USDA eradicated NWS from the United States in 1966 using sterile insect technique, a method where sterile flies are released in the wild. Today, NWS is endemic in Cuba, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, and countries in South America. There is a constant risk of introduction into the United States.
The name screwworm refers to the maggots' (larvae) feeding behavior as they burrow (screw) into the wound, feeding as they go like a screw being driven into wood. Maggots cause extensive damage by tearing at the hosts’ tissue with sharp mouth hooks. The wound can become larger and deepen as more maggots hatch and feed on living tissue. As a result, NWS can cause serious, often deadly damage to the animal. The cornerstone of this collaboration is the Panama-United States Commission for the Eradication and Prevention of Screwworm (COPEG). Through COPEG, we release sterile male screwworm flies in the Darian Province of eastern Panama to create a biological barrier.
NWS Outbreak in Central America
In 2023, NWS detections in Panama exploded from an average of 25 cases per year to more than 6,500 cases in 1 year. Screwworm were also detected in Costa Rica and Nicaragua, north of the biological barrier that’s successfully contained this pest to South America for decades.
APHIS is working with the U.S. Department of State, affected Central American countries, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, organizations like the Regional International Organization for Plant Protection and Animal Health (OIRSA) and the Inter-American Institute for Cooperation on Agriculture (IICA), and other USDA agencies to eradicate NWS in Central America and re-establish the biological barrier in the Darien Province of Panama.
The name screwworm refers to the maggots' feeding behavior as they burrow (screw) into the wound, feeding as they go like a screw being driven into wood. Maggots cause extensive damage by tearing at the hosts’ tissue with sharp mouth hooks. The wound can become larger and deepen as more maggots hatch and feed on living tissue. As a result, NWS can cause serious, often deadly damage to the animal.
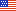
Adult screwworm flies are about the size of a common housefly (or slightly larger). They have orange eyes, a metallic blue or green body, and three dark stripes along their backs.
Report mammals and birds with the following signs:
- Irritated behavior
- Head shaking
- The smell of decay
- Evidence of fly strike
- Presence of fly larvae (maggots) in wounds
The best way to keep screwworm out of this country is to prevent introductions. NWS can infest mammals, including people, and birds. Here are steps you can take to avoid infestation:
- Be alert for NWS symptoms in pets and livestock.
- Ensure that pets traveling internationally are inspected for screwworm.
- Check your vehicle for screwworm flies if you are in an NWS-infested area.
If you think you have found a screwworm, report it immediately to your State animal health official and APHIS office. This will allow APHIS and partner agencies to respond quickly and remove the screwworms before a population becomes established.
Eradicating NWS is only possible through sterile insect technique. With this method, sterile flies are released into an area where a known population has become established. The sterile male screwworm flies mate with fertile female screwworm flies, causing the population of screwworm flies to decrease until it eventually dies out.
Animals infested with NWS should be treated according to the recommendations of their veterinarian. People who suspect they are infested with NWS should seek immediate medical treatment following the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines.
Report Signs of Animal Disease
Producers or owners who suspect an animal disease should contact their veterinarian to evaluate the animal or herd. Find an accredited veterinarian.
Animal health professionals (veterinarians; diagnostic laboratories; public health, zoo, or wildlife personnel; and others) report diagnosed or suspected cases of nationally listed reportable animal diseases to APHIS Area Veterinarians in Charge and to the State animal health official as applicable under State reporting regulations.
For information on how screwworms affect people or to report human disease, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:
Related Resources
United States
There are currently no known established populations of screwworm flies in the United States.
Central America
In 2023, APHIS detected and confirmed more than 6,500 New World screwworm (NWS) cases throughout Panama and Costa Rica. Before this, APHIS recorded an average of 25 cases per year.
APHIS International Services is partnering with other USDA agencies, the U.S. Department of State, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, and affected Central American countries to respond to the outbreak. In December 2023, APHIS announced $109.8 million in funds to combat new NWS detections in areas of Panama and Costa Rica that are critical to keeping the pest from spreading into North America. With this funding, APHIS aims to eradicate NWS in Central America and re-establish the biological barrier in the Darien Province.
Current Situation
The Panama-United States Commission for the Eradication and Prevention of Screwworm (COPEG) was created by cooperative agreement on February 11, 1994. Updated information on the current situation is available via the COPEG website.
In 2016, USDA confirmed an established population of NWS in Key Deer located on Big Pine Key, FL. USDA partnered with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services (FWS), Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services, and Florida’s Monroe County to prevent the spread of NWS, preserve the endangered deer, and protect domestic animals and pets. In 2017, USDA announced the successful eradication of NWS from Florida. Read more about the response below.
Watch a Time-Lapse Video of the 2016 Investigations in Florida
Sterile Fly Release
The USDA used a proven method for eradicating NWS fly populations that took advantage of the fly’s biology. Female screwworm flies mate one time in their 21-day lifespan. We released approximately 3 million sterile flies twice a week in the affected Florida Keys area. As the population of sterile NWS flies increased, fertile NWS flies decreased until the population died out. The USDA continued releasing sterile flies until there were no new clinical cases, and they eliminated the population of NWS flies.
The USDA continues to use this strategy to combat invasive species.
Screwworm Fly Surveillance
APHIS International Services worked with colleagues from Panama to monitor the success of the NWS fly eradication strategy. The team captured flies from across the Florida Keys and determined if they were sterile or fertile.
No fertile flies were found outside the infested zone in the lower Florida Keys, indicating a successful eradication strategy.
Animal Health Checkpoint
A mandatory animal health checkpoint was established at Mile Marker 106 in Key Largo to prevent NWS from leaving the Keys on pets or livestock.
Travelers with livestock or pets had to stop at the checkpoint and report any signs consistent with NWS. A veterinarian was assigned to the checkpoint to examine all suspect animals. The checkpoint was also a source of community outreach and education about NWS, the local infestation, the eradication strategy, and preventive measures to protect livestock and pets.
More than 6,000 animals traveled through the checkpoint; none were affected by NWS.
Animal Reports and Response
The USDA and Florida Department of Agriculture responded to reports of suspect wildlife, livestock (including poultry), and pets with clinical signs consistent with NWS infestation. There were no cases in livestock in the Keys, mainland, or outside of the infested Key islands.
Key Deer Monitoring and Response
The FWS, USDA, and the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services made significant efforts to protect endangered Key deer and other wildlife from infestation. The response focused on locating infested deer and administering medication, treating mild and moderate wounds by trained wildlife veterinarians, and in advanced cases, euthanizing deer for the animal’s welfare and to protect the remaining healthy deer and other wildlife.
FWS personnel and trained Refuge volunteers administered doramectin, an anti-parasitic medicine, to treat Key deer as a preventative measure. Additionally, FWS erected 27 self-medication stations in backcountry areas inaccessible to staff and volunteers. These self-medication stations became the main method of doramectin administration.
References
Disease Response Strategy: New World Screwworm Myiasis (763.71 KB)
Emergency Management: New World Screwworm
Fly Assessment Form (56.88 KB) (July 2017)
Fly Surveillance Site and Selection Methods (180.13 KB) (May 2017)
New World Screwworm: What You Need To Know (English (6.45 MB), Spanish (4.26 MB))
Screwworm: An International Threat to Human and Animal Health (958.86 KB)